October 2022
Inside the Newsletter:
Metal Fabrication | Water Efficiency | Jon Schroeder | Prescription Drug | Funding Opportunities
The Metal Fabrication Industry Spoke and MnTAP Listened
Over the past couple years, MnTAP has asked businesses in the metal fabrication industry about their general waste reduction practices. A total of 14 companies participated in these guided informational interviews focused on identifying successful best practices for pollution prevention and waste reduction as well as barriers to implementation. From these interviews, current areas of focus around waste reduction and pollution prevention were identified, as well as challenges found when implementing waste reduction strategies.
The following key findings were made regarding best practices and P2 opportunities among businesses in the sector:
Metalworking Fluid Management provides benefits including a longer fluid lifespan, improved product quality, increased cutting tool life and reduced coolant waste.
- Over 90% of respondents indicated they use water soluble emulsion for their machining operations
- 100% of respondents indicated they filter and/or reuse coolant which is a significant pollution prevention and cost saving action
- 75% of respondents continuously replenish coolant (daily or automated) or have a centralized system to maintain high quality and performance
- 50% of respondents use only one type of coolant with another 25% using two. The remaining 25% use 3 or 4 coolants and must dedicate effort to managing proper fluid use
Energy Efficiency is recognized as an important way to manage site utility costs.
- 100% of respondents indicated they have upgraded lighting at their facilities
- Most facilities have compressed air systems and recognize energy efficiency actions to be taken
- Machine monitoring and use of boiler economizers were cited as important energy actions
- All sites were aware of utility rebate programs to facilitate implementation of energy efficiency actions
Water Treatment is a common practice to achieve the high purity needed for coolant and cleaning.
- Use of water softening, reverse osmosis and deionization were cited by most facilities to manage water
- Optimizing these processes can save chemicals, energy, water and reduce waste generation
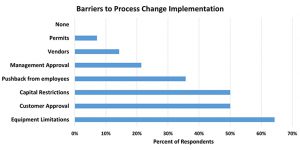 All respondents indicated a variety of challenges to implementing process changes. The top reasons include working within the constraints of current equipment, needing client approval for a change in the workflow or product design, or capital restrictions to purchase new equipment and/or management systems. Some waste reduction practices lose momentum over time if the perceived value is not worth the effort. This can be avoided by taking the time to assess the full benefit of a source reduction effort for a business. Capturing all the potential savings of an initiative prior to making a change and verifying these savings through trialing can reduce the information gap in assessing if a best practice is cost effective and sustainable.
All respondents indicated a variety of challenges to implementing process changes. The top reasons include working within the constraints of current equipment, needing client approval for a change in the workflow or product design, or capital restrictions to purchase new equipment and/or management systems. Some waste reduction practices lose momentum over time if the perceived value is not worth the effort. This can be avoided by taking the time to assess the full benefit of a source reduction effort for a business. Capturing all the potential savings of an initiative prior to making a change and verifying these savings through trialing can reduce the information gap in assessing if a best practice is cost effective and sustainable.
It is not too late to participate in a no cost site assessment targeting industries in metal manufacturing (NAICS 331) and metal fabrication (NAICS 332), especially metal fabrication, electroplating and electropolishing operations. MnTAP anticipates supporting at least two interns in summer 2023 in these industries.
This work is supported as part of the Pollution Prevention grant program sponsored by U.S. EPA Region 5 and the Minnesota Pollution Control Agency.
For More Information, Contact:
Daniel Chang – Associate Engineer
612-624-0808
dwchang@umn.edu
Water, Water Everywhere – Do We Really Need to Use So Much?
 Many communities here in the land of 10,000 lakes are evaluating the need to care for and conserve our precious water resources. Clean, reliable sources of water are critical to the vitality of our communities. Groundwater provides the drinking water for 75% of all Minnesotans and provides almost all of the water used to irrigate crops. Additional uses include commercial – our local shops and businesses, institutional – our healthcare facilities and schools, and industry – that provides needed products and employment. Recreational use and wildlife habitat also depend on our water resources. The DNR Water Availability and Assessment Report from 2020 highlights several observations from the study of water data from throughout the state.
Many communities here in the land of 10,000 lakes are evaluating the need to care for and conserve our precious water resources. Clean, reliable sources of water are critical to the vitality of our communities. Groundwater provides the drinking water for 75% of all Minnesotans and provides almost all of the water used to irrigate crops. Additional uses include commercial – our local shops and businesses, institutional – our healthcare facilities and schools, and industry – that provides needed products and employment. Recreational use and wildlife habitat also depend on our water resources. The DNR Water Availability and Assessment Report from 2020 highlights several observations from the study of water data from throughout the state.
- Minnesota’s climate is changing with more periods of drought anticipated.
- Water use in non-power generation activities declined from 2007-2019 from adoption of water saving technologies, increasing industrial water reuse and use of irrigation best practices.
- Groundwater is limited in some regions of the state due to poor producing or slow charging aquifers that may not keep pace with local use rates.
Communities may also be facing water availability challenges due to aquifer contamination or aging infrastructure that is unable to reliably keep up with community water demand.
MnTAP and Minnesota Rural Water Association (MRWA) are partnering to support no cost assistance for water efficiency in Minnesota cities. The program provides training and technical assistance resources to help your community and your business evaluate the best way to start, continue or improve your water conservation efforts. MnTAP and MRWA will:
- Work to address your priorities and conservation targets
- Present water conservation workshops geared towards your target audience
- Conduct outreach to local high water users to offer assistance
- Assess sites to find opportunities and perform savings analysis
- Collaborate to identify cost-effective solutions
Water efficiency projects often have additional benefits that result from a decrease in water use. Recommendations made by 2021 interns focused on water efficiency projects included 18,000 lbs of chemical use avoided, 31,000 therms of natural gas energy and 655,000 kWh of electric energy reduced. These co-benefits carry an additional $52,700 in first-year cost savings above the cost of the water itself. The cost savings from additional chemical or energy reductions associated with water efficiency can help justify investments that may be needed for full project implementation.
If you are interested in bringing resources to your community or business to explore your water conservation opportunities, check out the project website and fill in the form or contact MnTAP directly.
For More Information, Contact:
Laura Sevcik – Associate Engineer
612-624-8192
lsevcik@umn.edu
Acknowledgement
The authors would like to acknowledge support for this project by the Minnesota Rural Water Association and the Minnesota Environment and Natural Resources Trust Fund as recommended by the Legislative-Citizen Commission on Minnesota Resources (LCCMR). The Trust Fund is a permanent fund constitutionally established by the citizens of Minnesota to assist in the protection, conservation, preservation, and enhancement of the state’s air, water, land, fish, wildlife, and other natural resources. Currently 40% of net Minnesota State Lottery proceeds are dedicated to growing the Trust Fund and ensuring future benefits for Minnesota’s environment and natural resources.
MnTAP Welcomes Jon Schroeder
 Jon’s professional passion lies in all areas of sustainability, but particularly food waste. Jon holds a Bachelor of Science in Business from the Carlson School, University of Minnesota and a Master of Science in Sustainable Systems from Golisano Institute for Sustainability, Rochester Institute of Technology. He brings several years of sustainability experience spanning various settings including the private sector, government, academia, and a startup. He has been a key member of projects involving collection and analysis of waste data, compiling tools related to food waste reduction and assessing environmental impacts of products and processes through life cycle analysis.
Jon’s professional passion lies in all areas of sustainability, but particularly food waste. Jon holds a Bachelor of Science in Business from the Carlson School, University of Minnesota and a Master of Science in Sustainable Systems from Golisano Institute for Sustainability, Rochester Institute of Technology. He brings several years of sustainability experience spanning various settings including the private sector, government, academia, and a startup. He has been a key member of projects involving collection and analysis of waste data, compiling tools related to food waste reduction and assessing environmental impacts of products and processes through life cycle analysis.
Jon will be using his broad experience working on many material-related topics in his new role with MnTAP. Part of his responsibility will be leading efforts to increase reuse within the state by refreshing and expanding the impact of the Minnesota Materials Exchange. Jon has already started directly interfacing with companies looking to reduce both food and nonhazardous waste generation through site visit activities. Feel free to contact Jon with any of your food waste reduction, recycling, and reuse questions.
Jon Schroeder – Sustainable Materials Management Specialist
612-624-6456
jschro@umn.edu
Prescription Drug Take Back Day
Saturday, October 29, 2022
Twice per year, the U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) sponsors a National Prescription Drug Take Back Day in an effort to limit abuse and ensure proper disposal of prescription medication. Proper drug disposal can also prevent pollution, as components of prescription drugs have been detected in surface waters in recent years.
If you have expired or no longer needed medication in your possession, don’t just flush it down the drain – protect the environment and those around you by following the DEA’s guidance.
The next Take Back Day is this Saturday, October 29 – you can find more information and a drop-off location near you at DEA National Take Back.
Funding Opportunities
Greater Minnesota Recycling and Composting Grants
MPCA is seeking projects that increase the efficiency or effectiveness of reuse, recycling, or composting programs. Reducing the amount of recyclable and compostable materials entering landfills in Greater Minnesota communities benefits the environment as well as local economies.
Awards:
-
- Available Funding: Approximately $1 million
- Minimum Award: $150,000
- Maximum Award: $250,000
- At least 25% match required
Eligible Applicants:
-
- Minnesota counties, cities, townships, and Tribes located outside of the Twin Cities metro area may apply. Cities must have a population of less than 45,000.Application
Application Deadline:
-
- Tuesday, November 15, 2022, 4:00 pm
- Online application through SWIFT
Dry Cleaner Cost Share Program
Minnesota has banned the use of Perchloroethylene (perc) as a dry-cleaning solvent starting in 2026. This cost share funding can help your dry-cleaning business switch away from perc.
Awards:
-
- Up to $20,000 per applicant
- Awards will be made to eligible applicant on a first come, first served basis. Early application improves the chance of funding availability.
Eligible Applicants:
-
- Owners/operators of dry cleaning facilities in Minnesota that use or are eliminating PERC.
- Eligible projects must eliminate PERC.
Application Deadline:
-
- Monday April 1, 2024
- The RFP will remain open and application accepted on a rolling basis until all dedicated funds have been dispersed, whichever comes first.
Applicants are encouraged to take advantage of matching fund opportunities such as the MPCA Small Business Loan Program which covers equipment costs up to $75,000 at 0% interest.
If you are a small dry-cleaning business owner and would like assistance applying for this grant, please contact MnTAP at 612-624-1300 or email MnTAP at mntap@umn.edu and leave your contact information.



